Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Optics and Optical Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
2 Advanced Laser Technology Laboratory of Anhui Province, Hefei 230026, China
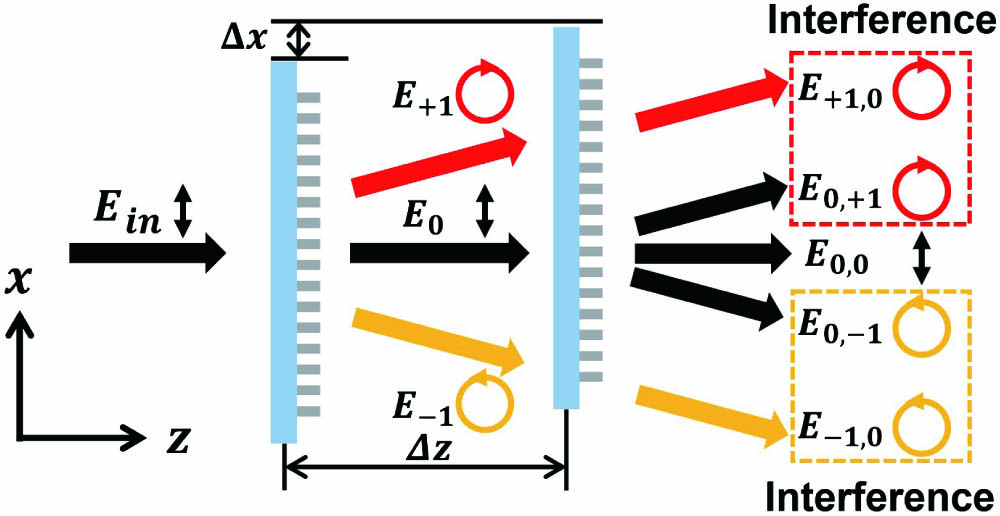
The compact, sensitive, and multidimensional displacement measurement device plays a crucial role in semiconductor manufacture and high-resolution optical imaging. The metasurface offers a promising solution to develop high-precision displacement metrology. In this work, we proposed and experimentally demonstrated a two-dimensional displacement (XZ) measurement device by a dielectric metasurface. Both transversal and longitudinal displacements of the metasurface can be obtained by the analysis of the interference optical intensity that is generated by the deflected light beams while the metasurface is under linearly polarized incidence. We experimentally demonstrated that displacements down to 5.4 nm along the x-axis and 0.12 µm along the z-axis can be resolved with a 900 µm × 900 µm metasurface. Our work opens up new possibilities to develop a compact high-precision multidimensional displacement sensor.
metasurface transversal and longitudinal displacement measurement Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(2): 021202
1 航天工程大学, 北京 101416
2 中国人民解放军63920部队, 北京 100094
3 北京跟踪与通信技术研究所, 北京 100094
随着“2020 SO身份之谜”的落幕, 空间目标的光谱表征及识别技术在空间领域感知中的地位再次凸显。 光谱表征及识别技术的突出优点是能够通过空间目标表面反射的光谱识别出其材料, 进而确认空间目标的身份及类型。 该技术在图像不具备空间分辨率的前提下, 仍然能够较准确地识别出材料, 因此通过低成本小口径望远镜进行空间目标材料表征的可行性得到验证。 在这一点上, 传统的观测手段很难做到的。 2000年, Jorgensen的博士论文在该领域内引起了广泛的关注, 从此开启了空间目标光谱表征的研究热潮。 然而, 经历了20余年的发展, 空间目标的光谱表征及识别技术在实际应用中仍然受到了较大的限制, 这与空间目标的光谱表征方式以及空间环境的复杂性和未知性有着较大的关系。 研究者们通常以地面实验室内的测量数据为依据对实际在轨目标进行表征和识别, 而空间环境的作用却导致了两种测量结果之间存在着无法被描述的差异。 光谱解混法是空间目标材料识别的主流方法, 对其原理和应用情况进行了详细的介绍, 并指出实验室测量结果与实测结果之间的差异是造成解混不成功的主要原因。 解混识别的准确率很大程度上取决于光谱数据库的完善程度, 因此在建立光谱数据库时需要重点考虑空间环境和观测几何对空间目标光谱特性的影响。 同时, 人工智能算法的引入也将大大提高空间目标光谱表征及识别的能力。 从空间目标光谱特性及分类研究、 空间目标材料表征及识别研究、 空间目标光谱的红化现象、 光谱数据库的发展情况四个方面进行了详细的综述及讨论, 分析了其中的难点和重点问题, 凝练出了一些具有参考价值的建设性意见, 希望能够给广大研究者提供便利。
空间目标 光谱表征 材料识别 红化 解混 Space object Spectral characterization Material identification Reddening Unmixing 光谱学与光谱分析
2023, 43(5): 1329
树木的量化模型对分析树木拓扑结构和生物量等信息非常重要。树木定量结构模型(TreeQSM)作为主流建模方法,被广泛使用,但在估计树高、胸径和体积的精度上缺少全面分析。实验中用地面激光雷达多扫描角分辨率多站点扫描2棵模型树和5棵真实杏树,通过TreeQSM建模单站和多站融合数据估计得到较精确的树高、胸径和体积参数,同时分析不同角度分辨率、不同站点数量对估计树高、胸径和体积的影响。实验结果表明:树高和胸径的平均估计精度均在90%以上;对树木体积而言,结构较为简单的模型树平均估计精度为92.00%,结构较为复杂的真实杏树平均估计精度71.32%。由实验数据可知,扫描角分辨率和融合站数对精度有一定的影响,且不同参数最优估计结果的配置存在差别,同时TreeQSM也会受到点云数据基础、数据完整性和噪声等多因素影响,特别是针对复杂分枝结构和体积进行建模时仍存在一定的偏差,所提模型的改进空间巨大。
遥感 地面激光雷达 定量结构模型 点云 树木重建 中国激光
2023, 50(22): 2210003
1 山东大学, 新一代半导体材料研究院, 晶体材料国家重点实验室, 济南 250100
2 山东工业技术研究院, 济南 250100
本文研究了斜切角的引入对β-Ga2O3(100)面衬底加工的影响, 分析了斜切角分别为0°、1°、6°时, (100)面衬底在加工过程中的形貌变化及不同抛光参数对衬底抛光的影响。实验结果表明, 随着斜切角的增大, (100)面衬底在加工过程中的解理损伤问题得以改善, 加工后表面粗糙度降低, 材料去除方式出现了脆性去除-脆塑性混合去除-塑性去除的转变。较小的抛光压力可以有效减少解理损伤, 改善表面质量。斜切角为6°时的(100)面衬底抛光效率高, 抛光后表面粗糙度可达到Ra≤0.2 nm。
解理 斜切角 抛光 表面粗糙度 β-Ga2O3 β-Ga2O3 cleavage miscut-angle polishing surface roughness
1 山东大学,晶体材料国家重点实验室,新一代半导体材料研究院,晶体材料研究院,济南 250100
2 山东省工业技术研究院,济南 250100
β-Ga2O3作为最具发展潜力的超宽禁带半导体材料,其晶体缺陷方面还缺乏深入且全面的研究。面缺陷小角晶界主要存在于β-Ga2O3 (100)晶面,会破坏晶体结构完整性,降低晶体质量。采用化学刻蚀法和透射电子显微镜技术对导模法生长β-Ga2O3晶体中的小角晶界进行宏观分析和微观结构表征。研究表明:小角晶界两侧的刻蚀坑形状和朝向相同,晶界两侧的晶粒取向差约为3°,除此之外,小角晶界会使摇摆曲线出现肩峰及展宽,通过对β-Ga2O3晶体中小角晶界缺陷的微观结构进行表征,填补了小角晶界缺陷的研究空白。
导模法 β-氧化镓 小角晶界 摇摆曲线 edge-defined film-fed growth method β-gallium oxide low angle grain boundaries rocking curve

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Optics and Optical Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
2 Key Laboratory of Materials for High-Power Laser, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
3 Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou 310024, China
4 e-mail: hongxingd@siom.ac.cn
5 e-mail: lzhang@siom.ac.cn
Optical physical unclonable functions (PUFs) have emerged as a promising strategy for effective and unbreakable anti-counterfeiting. However, the unpredictable spatial distribution and broadband spectra of most optical PUFs complicate efficient and accurate verification in practical anti-counterfeiting applications. Here, we propose an optical PUF-based anti-counterfeiting label from perovskite microlaser arrays, where randomness is introduced through vapor-induced microcavity deformation. The initial perovskite microdisk laser arrays with regular positions and uniform sizes are fabricated by femtosecond laser direct ablation. By introducing vapor fumigation to induce random deformations in each microlaser cavity, a laser array with completely uneven excitation thresholds and narrow-linewidth lasing signals is obtained. As a proof of concept, we demonstrated that the post-treated laser array can provide fixed-point and random lasing signals to facilitate information encoding. Furthermore, different emission states of the lasing signal can be achieved by altering the pump energy density to reflect higher capacity information. A threefold PUF (excited under three pump power densities) with a resolution of pixels exhibits a high encoding capacity (), making it a promising candidate to achieve efficient authentication and high security with anti-counterfeiting labels.
Photonics Research
2023, 11(7): 1227
湖北师范大学 物理与电子科学学院, 湖北 黄石 435002
该文介绍了一种基于马赫-则德尔干涉仪(MZI)与二甲基硅油(DSO)相结合的高灵敏度光纤温度传感器。传感器由MZI及填充在其表面的DSO组成。MZI由单模光纤-锥形无芯光纤-单模光纤构成。填充DSO后,MZI的谐振峰向右有小的漂移。通过跟踪MZI谐振峰波长随温度的变化,对环境温度进行测量。经测试,传感器的温度灵敏度为-97.7 pm/℃,而未填充DSO的MZI温度灵敏度为-50.1 pm/℃,传感器灵敏度提高了约1.95倍。该传感器具有结构制作简单,造价低及灵敏度高等优点,具有一定的应用前景。
光纤温度传感器 马赫-则德尔干涉仪(MZI) 二甲基硅油(DSO) 无芯光纤 光纤拉锥 fiber optic temperature sensor Mach-Zehnder interferometer (MZI) dimethyl silicone oil (DSO) no-core fiber fiber tapering

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Advanced Laser Technology Laboratory of Anhui Province, Department of Optics and Optical Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
2 Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
3 Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Photonics Technology, College of Photonic and Electronic Engineering, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou 350117, China
4 e-mail: leigong@ustc.edu.cn
5 e-mail: dgzhang@ustc.edu.cn
Opto-thermophoretic manipulation is emerging as an effective way for versatile trapping, guiding, and assembly of biological nanoparticles and cells. Here we report a new opto-thermophoretic tweezer based on an all-dielectric one-dimensional photonic crystal (1DPC) for reversible assembly of biological cells with a controllable center. To reveal its ability of long-range optofluidic manipulation, we demonstrate the reversible assembly of many yeast cells as well as E. coli cells that are dispersed in water solution. The 1DPC-based tweezer can also exert short-range optical gradient forces associated with focused Bloch surface waves excited on the 1DPC, which can optically trap single particles. By combining both the optical and thermophoretic manipulation, the optically trapped single polystyrene particle can work as a controllable origin of the reversible cellular assembly. Numerical simulations are performed to calculate the temperature distribution and convective flow velocity on the 1DPC, which are consistent with the experimental observations and theoretically confirm the long-range manipulations on the all-dielectric 1DPC platform. The opto-thermophoretic tweezers based on all-dielectric 1DPC endow the micromanipulation toolbox for potential applications in biomedical sciences.
Photonics Research
2022, 10(1): 01000014
1 1.深圳大学 增材制造研究所, 深圳 518060
2 2.广东省电磁控制与智能机器人重点实验室, 深圳 518060
3 3.华中科技大学 材料科学与工程学院, 材料成形与模具技术国家重点实验室, 武汉 430074
4 4.华中科技大学 增材制造陶瓷材料教育部工程研究中心, 武汉 430074
陶瓷以其优异的热物理化学性能在航空航天、能源、环保以及生物医疗等领域具有极大的应用潜力。随着这些领域相关技术的快速发展, 其核心零件部件外形结构设计日益复杂、内部组织逐步走向定制化、梯度化。陶瓷具有硬度高、脆性大等特点, 较难通过传统的加工成形方法实现异形结构零件的制造, 最终限制了陶瓷材料的工程应用范围。激光增材制造技术作为一种快速发展的增材制造技术, 在复杂精密陶瓷零部件的制造中具有显著优势: 无模、精度高、响应快以及周期短, 同时能够实现陶瓷零件组织结构灵活调配, 有望解决上述异形结构陶瓷零件成形问题。本文综述了多种基于粉末成形的激光增材制造陶瓷技术: 基于粉末床熔融的激光选区烧结和激光选区熔化; 基于定向能量沉积的激光近净成形技术。主要讨论了各类激光增材陶瓷技术的成形原理与特点, 综述了激光选区烧结技术中陶瓷坯体后处理致密化工艺以及激光选区熔化和激光近净成形技术这两种技术中所打印陶瓷坯体基体裂纹开裂行为分析及其控制方法的研究进展, 对比分析了激光选区烧结、激光选区熔化以及激光近净成形技术在成形陶瓷零件的技术特征, 最后展望了激光增材制造陶瓷技术的未来发展趋势。
激光增材制造 激光选区烧结 激光选区熔化 激光近净成形技术 陶瓷 综述 laser additive manufacturing selective laser sintering selective laser melting laser engineered net shaping ceramic review





